Recent datasets
Towed Video surveys down to a depth of ~50 m was completed successfully at the following shoals (Baracuda East, Goeree Shoal, Vulcan Shoal). Sampling involved habitat classification conducted in real-time during the surveys, and taking photographic still image at 5s intervals for subsequent analysis as the cameras were towed across the shoals at a speed of 1-2 knots.
This project is a co-investment between PTTEPAA and AIMS, in order to build scientific knowledge on a number of shoal features in the area near Montara and was undertaken between 19/9/2016 - 24/9/2016.
A total of 365 towed video transects were completed in the 2006/2007 surveys. The sampling has identified a vast array of habitats and will be used for broad scale mapping of benthic communities in the marine park, however further transect tows will be conducted in 2008 in areas of special interest, where sampling is considered limited and where ground-truthing is required. Towed video sampling effort was concentrated around Mandu, Osprey, Yardie, Winderabandi and Point Cloates in 2006.
Stereo Baited Remote Underwater Video Stations (BRUVS) were successfully deployed and retrieved at each of the 3 shoals (Baracuda East , Goeree Shoal, Vulcan Shoal). Deployments were restricted to 250 m. In general 24 stereo BRUVS were deployed at each shoal.
This project is a co-investment between PTTEPAA and AIMS, in order to build scientific knowledge on a number of shoal features in the area near Montara and was undertaken between 19/9/16 - 24/9/16.
This metadata record describes salinity and temperature time-series data collected through in situ monitoring by the Great Barrier Reef Marine Monitoring Program for Inshore Water Quality (MMP WQ). A full description of the MMP WQ and its associated datasets can be found in the parent metadata record linked above.
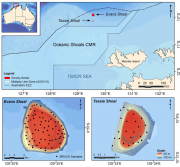
Stereo Baited Remote Underwater Video Stations (BRUVS) were deployed and retrieved across two shoals of regional interest, Evans and Tassie Shoals, two of the closest shoals to the Barossa field. The allocation of deployment positions across each shoal was conducted using a regular/random design within the bounds of the 60 m depth contour whilst maintaining a minimum distance of 250 m between each stereo-BRUVS unit. Once the positions were derived, the sequence of deployments, in sets of eight replicate units, was determined by proximity and prevailing sea conditions on the day.
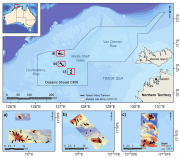
Towed video surveys were carried out in targeted shallow seabed environments within the proposed Oceanic Shoals Commonwealth Marine Reserve (CMR) in the Timor Sea. The survey concentrated on shelf habitats (< 200m) of the western part of the Oceanic Shoals CMR and included potential biodiversity hotspots such as pinnacles, banks and shoals. In total, 52 towed video transects were collected at depths of between 31 and 129 metres.
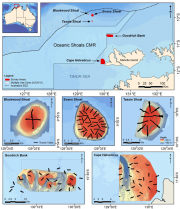
Towed video surveys were carried out across five principle locations of regional interest, including Evans, Tassie and Blackwood Shoals, the closest shoals to the Barossa field, as well as two mid-shelf seabed locations adjacent to Goodrich Bank and Cape Helvetius. In total, 113 towed video transects and 2246 downward facing digital still images were collected at depths of between 11 and 100 metres.
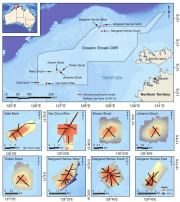
Towed video surveys between were carried out in targeted shallow seabed environments within and adjacent to the proposed Oceanic Shoals Commonwealth Marine Reserve (CMR) in the Timor Sea. The survey concentrated on shelf habitats (< 200m) of the Oceanic Shoals CMR and included potential biodiversity hotspots such as pinnacles, banks and shoals. In total, 48 towed video transects were collected at depths of between 17.2 and 89 metres.
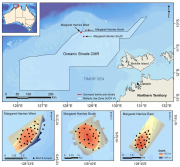
Stereo Baited Remote Underwater Video Stations (BRUVS) were deployed and retrieved across targeted shallow seabed environments within and adjacent to the proposed Oceanic Shoals Commonwealth Marine Reserve (CMR) in the Timor Sea. The survey concentrated on shelf habitats (< 200m) of the Oceanic Shoals CMR and included potential biodiversity hotspots such as pinnacles, banks and shoals.
Towed video surveys were carried out in targeted shallow seabed environments within the proposed Oceanic Shoals Commonwealth Marine Reserve (CMR) in the Timor Sea. The survey concentrated on shelf habitats (< 200m) of the western part of the Oceanic Shoals CMR and included potential biodiversity hotspots such as pinnacles, banks and shoals. In total, 52 towed video transects were collected at depths of between 31 and 129 metres.
Stereo-Baited Remote Underwater Video Stations (BRUVS) were deployed and retrieved in targeted shallow seabed environments within the proposed Oceanic Shoals Commonwealth Marine Reserve (CMR) in the Timor Sea. The survey concentrated on shelf habitats (< 200m) of the western part of the Oceanic Shoals CMR and included potential biodiversity hotspots such as pinnacles, banks and shoals. In total, 56 stereo-BRUVS were deployed between 31 and 77 metres for one hour according to a regular random sampling design, with minimum spacing of 400 m to ensure independence among samples.

In NW Australia a range of emergent reefs bound the western margin of the Oceanic Shoals bioregion, but with the major feature being numerous submerged shoals lying along and across the shelf edge. Scott Reef, the largest emergent reef system, has a diverse shallow water coral reef ecosystem that has demonstrated impressive resilience to cyclone and coral bleaching disturbances over the last 15 years (Gilmour et al, 2013). The adjacent deeper lagoon of South Scott Reef covers approximately 300 km2 in depths of 30-?70m.
This layer shows a 500m resolution image of the world derived from the Blue Marble Next Generation April 2004 image (86400x43200 pixels).
As the image was derived from MODIS satellite imagery during Autumn in the Northern Hemisphere the high latitude countries (Russia, Canada, etc) are covered in snow.
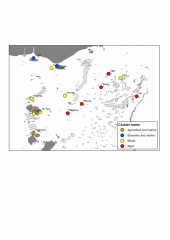
Determining the impact on Torres Strait communities from future changes to ecosystems requires an understanding of the natural resource base that underpins their livelihoods. To do this, we estimate the relative importance of natural resources, or ecosystem goods and services (EGS) to local livelihoods, which in turn is a function of the relative volume of those EGS, and their relative value to human well-being. Our approach was focused on 'provisioning' and 'cultural' EGS, which have a direct link to local livelihoods.
This dataset consists of summaries of benthic, fish and manta tow surveys conducted in the Capricorn-Bunker Region of the Great Barrier Reef in October 2015. It consists of three tables:
This metadata record describes chlorophyll fluorescence and turbidity time-series data collected through in situ monitoring by the Great Barrier Reef Marine Monitoring Program for Inshore Water Quality (MMP WQ). A full description of the MMP WQ and its associated datasets can be found in the parent metadata record linked above.

Despite the important role Symbiodinium might play we currently have limited knowledge of the distribution ranges of Symbiodinium on the Great Barrier Reef.
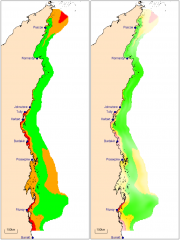
The purpose of this study was threefold: (1) to identify water quality guideline values based on existing ecological data; (2) to identify areas where guidelines are met or exceeded, and (3) to quantify the likely ecological changes associated with improving water quality to meet the guidelines.
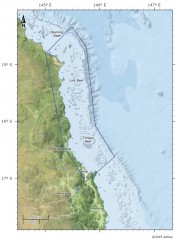
This dataset corresponds to a shapefile that defines the COTS initiation zone for use in the evaluation of the merit of investment in surveillance and cull and reducing agricultural run off.
The COTS box is a speculative area of primary outbreaks of Crown-of-Thorns Starfish.
This polygon includes Lizard island to the north and Green Island in the south.
Methods:
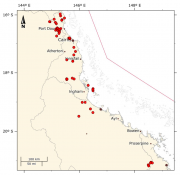
This dataset consists of 546 records of vertebrate species across various sites in the rainforests and adjacent habitats of the Wet Tropics and the Eungella region. Surveys particularly targeted threatened frogs and focussed on ecotonal and peripheral rainforest areas. Each record consists of the date, species, locality name, latitude and longitude, habitat, and observer.



