Recent datasets
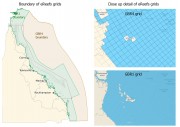
This dataset consists of shapefiles that correspond to the model grids used in the CSIRO eReefs hydrodynamic and biogeochemical models. These models store their results in multi-dimensional NetCDF files using a curvilinear grid. This dataset corresponds to an extract from these files converting the curvilinear grid into polygons in a shapefile. This dataset only captures the structure of the grid, not the time series data generated by the model.

This dataset consists of 1 excel data files (.xlsx format) that contains the results from the in situ deployment of instruments in Cleveland Bay to measure sediment deposition from a trailer suction hopper dredge working in Platypus channel. The aim of the study was to measure sediment deposition rates caused by a working Trailer Suction Hopper dredge in Platypus channel in Cleveland Bay.

This dataset consists of one data file (spreadsheet) from a 28-d experiment examining sediment-induced changes in the spectral quality and quantity of light on three coral species (Acropora millepora, Pocillopora verrucosa and Montipora aequituberculata) and one encrusting sponge species (Cliona orientalis).

This dataset resulted from two inter-linked research streams. The first stream was related to the application of eye-tracking technology and an online survey in studying natural beauty. The second stream is related to the development of an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based system recognising and assessing the beauty of natural scenes. Due to differences in data collection and data analysis, details of research methods used for each research stream are described in three separated data records.
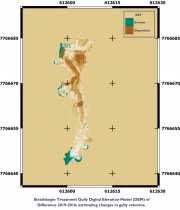
Five paired Control/Treatment gully sites on commercial grazing properties in the Upper Burdekin and Bowen catchments are being monitored as part of NESP Project 2.1.4 (Demonstration and evaluation of gully remediation on downstream water quality and agricultural production in GBR rangelands) (Bartley et al., 2018).
The key question being asked is: "Is there measurable improvement in the erosion and water quality leaving remediated gully sites compared to sites left untreated?" The monitoring approach uses a modified BACI (Before after control impact) design.
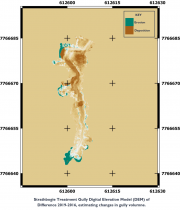
This dataset contains Riegl terrestrial laser scanner scans and their derived 5 cm gridded digital elevation models (DEMs) collected for up to 4 years between 2016 and 2019 for 4 paired Control/Treatment gully sites being monitored as part of NESP Project 2.1.4. Data collection also contains the DEMs of difference used to estimate changes in gully volume.

The aim of the study was to obtain light and turbidity vertical profile data through the water column in Cleveland Bay over a four-day period and during maintenance dredging to use for developing an empirical spectral solar irradiance model.
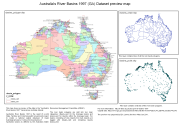
Australia's River Basins 1997 is the result of a joint State, Territory and Commonwealth Government project to create a national spatial database of major hydrological basins. It shows the boundaries of Australia's basins as defined by the Australian Water Resources Management Committee (WRMC).
Australia is divided into drainage divisions which are sub-divided into water regions which are in-turn sub-divided into river basins. The data includes the name and number of each of the 245 drainage basins, 77 regions, and 12 divisions.

This dataset contains preliminary estimates of discharge and loads (Total suspended sediment and total nitrogen) based on monitoring data collected for the NESP Project 2.1.4 Demonstration and evaluation of gully remediation on downstream water quality and agricultural production in GBR rangelands.
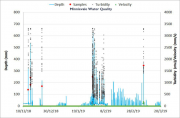
This dataset contains Water Quality monitoring data collected at the project gully sites for the three reporting wet seasons 2016-2017, 2017-2018 and 2018-2019.
The data in presented in this metadata are part of a larger collection and are intended to be viewed in the context of the project. For further information on the project, view the parent metadata record: Demonstration and evaluation of gully remediation on downstream water quality and agricultural production in GBR rangelands (NESP TWQ 2.1.4, CSIRO).
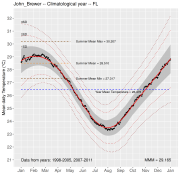
The climatology of the GBR temperature loggers is based on the hourly registers from loggers with 10 or more years of data, up to 2012 and for "Slope" and "Flat" locations on the reef.
The climatology is important as a reference point for comparison of future values. It also allows to compute the anomalies which represent the deviations from an established baseline. The data comes from the AIMS temperature loggers program and contains temperature registers as old as from 1991, providing for some sites, a time series of water temperature for more that 28 years.
The Biophysical Oceanography Group produces monthly oceanographic reports for the eastern Australian coast, including the Torres Strait, which summarise key environmental variables such as sea surface temperature (SST) and chlorophyll concentration. These variables are important indicators for coral reef ecosystems and other biological processes.
This series of the reports covers from August 2011 - November 2014
This research was conducted to understand the relationship between water quality and ecological attributes on coral reef communities, through field surveys on naturally turbid inshore coral reefs that vary in exposure to water bourne sediment, nutrient and chlorophyll concentrations. Reefs in two regions were surveyed for biodiversity of algae, hard corals, octocorals and fish. Region PC: Princess Charlotte Bay (in the Claremont Isles, north of PC Bay) and and Region WT: Wet Tropics (between Tully and Port Douglas).
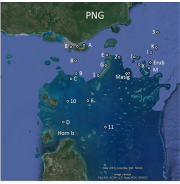
This dataset summarises the results of a survey to determine the concentration of trace metals from mine-derived pollution in marine waters and sediments across the Torres Strait during October 2016. Sampling was performed by a CSIRO team between 3 and 16 October 2016 on board the MV Eclipse. Surface water samples were collected from 21 sites using strict sampling protocols that are designed to minimise contamination (USEPA, 1996; Angel et al., 2010b).
METHODS:

This dataset summarises the results of a survey of water quality and suspended solid metal data for ten (10) sites around Saibai and Boigu Islands in the Torres Strait during November 2018. This is the second survey for this project, where the first survey identified the area around Saibai as having elevated metal concentrations compared to other areas of the Torres Strait. This survey was conducted to investigate this finding. Water samples were collected from five sites around Saibai Island and five sites around Boigu Island.
METHODS:

This dataset shows the measured response of early life history stages to different levels of nutrient enrichment and temperatures in experiments conducted in 2014-2015.
The data is presented as one Excel spreadsheet file. Each tab contains data from experiments (Exp. 1a,b; Exp 1c,d; Exp. 2; Exp 3) on different life stages exposed to the same conditions. Measured logged water quality (Nutrients) and temperature (Temperature) data taken during the experiment are also presented in different tabs.

This dataset consists of one data file presenting data from 4 experiments conducted under aquarium controlled conditions manipulating levels of suspended sediments, temperature and nutrient enrichment. The experiments measured the conditions effect on early life history stages like gamete fertilisation success, embryo development, larval survivorship and larval settlement of the coral Acropora tenuis.
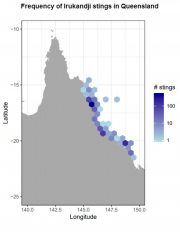
This dataset presents the code written for the analysis and modelling for the Jellyfish Forecasting System for NESP TWQ Project 2.2.3. The Jellyfish Forecasting System (JFS) searches for robust statistical relationships between historical sting events (and observations) and local environmental conditions. These relationships are tested using data to quantify the underlying uncertainties. They then form the basis for forecasting risk levels associated with current environmental conditions.
This dataset consists of a shapefile of the reefs, islands, sand banks, cays and rocks of the whole Great Barrier Reef (GBR) including Torres Strait. This dataset is an extension of the mapping in the GBR Marine Park to include Torres Strait. The Torres Strait region was mapped at a scale of 1:50,000 (Lawrey, E. P., Stewart M., 2016) and these new features are referred to as the "Torres Strait Reef and Island Features" dataset.
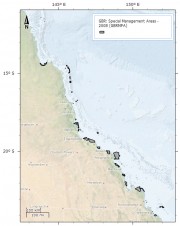
This dataset contains the amalgamated set of Special Management Areas (SMAs) in the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park as described in the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Regulations 1983, Amendments 2008. This includes:
SMA - No Dories Detached,
SMA - Princess Charlotte Bay,
SMA - Public Appreciation,
SMA - Restricted Access,
SMA - Seasonal Closure,
SMA - Dugong Protection Area B,
SMA - Dugong Protection Area A,
SMA - Natural Resources Conservation
Dugong Protection Areas:



