Recent datasets

This dataset contains telephone (n=1743), mail (n=800), and face-to-face (n=132) survey data collected from the recreational fishing community in the Great Barrier Reef region. The surveys were aimed primarily at understanding fishers' attitudes and perceptions regarding the 2004 rezoning of the GBR and the impacts of the new zoning plan on recreational fishing activity and the spatial distribution of recreational fishing effort.
This dataset consists of site and zone means of the percent cover of major benthic categories and the density of fish functional groups on fringing coral reefs of the Keppel, Whitsunday and Palm Island groups, as a result of monitoring surveys carried out between 1999 and 2014.
This data extract summarises the results of a long-term monitoring project that assesses the effects of no-take marine reserve zoning in the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park.
This project will conduct a biodiversity assessment of coral communities on Torres Strait reefs to establish a baseline of coral condition and start a longer-term monitoring program of selected coral reefs in the region. The monitoring will look for changes in the condition of coral reefs and document factors that might contribute to changes incl COTS, disease, bleaching, temperature anomalies etc. As part of this project, an early warning system will be established for coral bleaching.

The purpose of this study was to quantify patterns in scleractinian biodiversity, and in the cover of the main benthos groups, on the Great Barrier Reef. Taxonomic surveys of hard corals conducted on 110 reefs (599 transects) of the GBR between 1994 and 2001. Surveys are based on rapid ecological assessments (taxonomic inventories based on swim surveys) conducted at two depth zones (deep and shallow), typically at two sites per reef. The data are abundance estimates of each species. Richness is calculated based on reef-averaged data.

This dataset shows the measured response of the photosystems of seagrasses to herbicides in experiments conducted in 2014. The purpose of the experiments were to develop and validate a miniature toxicity assay using isolated seagrass leaves in 12-well plate.

Depth and Elevation Model of the Great Barrier Reef (GBRDEM), a regional-scale terrain model covering the Great Barrier Reef, catchments which flow into the Great Barrier Reef and, where data are available, depths beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Data are presented as Mean Sea Level (MSL, unit: m), a measure indistinguishable from the Australian Height Datum (AHD) in accuracy at the regional scale.

This dataset consists of an atlas of the habitat quality of the urbanized and agricultural landscapes of the Mission beach region in August 2006, 6 months after cyclone Larry. This analysis and classification includes habitat quality, canopy cover, vegetation quality, vegetation types, tenure type and aerial photography at a resolution of 0.5m.
These maps of habitat quality highlight potential priority areas for maintenance and/or restoration of connectivity and is a tool for natural resource managers to implement restoration goals at Mission beach.
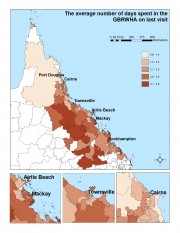
This data set in excel sheet format presents results of the mail survey of 1565 residents of the GBRWHA. The dataset is accompanied by a set of 58 maps that illustrate key findings.
Project 10.2 explored how visitors and residents feel towards and perceive Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area, as well as their willingness to pay to protect the reef and their satisfaction with current and future developments in and around the GBRWHA.

This data set contains life history data from 46 species of coral reef fish from four families (see list below). The data and samples on which these analyses are based were collected as part of the Effects of Line Fishing Project and the East Torres Strait Coral Reef Fishery Project. Species included in this data set include:
Labridae: Cheilinus undulatus, Choerodon cyanodus, C. fasciatus, C. schoenleinii, C. venustus
Lethrinidae: Lethrinus atkinsoni, L. lentjan, L. nebulosus, L. olivaceus

Pattern of seagrass distribution in the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area

This study characterises spatial patterns in water clarity. Water clarity is a key indicator for water quality and is an essential environmental factor for phototrophic organisms that dominate coral reefs, seagrass meadows and the seafloor microphytobenthos. Secchi disk depthis a commonly used standardised way to quantify water clarity.

The purpose of this study was to characterise spatial and temporal patterns in sea surface temperatures in the Great Barrier Reef.

Trajectories of decline have been observed in coral reefs throughout the Caribbean and Indo-Pacific region attributable to the synergistic effects of human-induced disturbances. Whilst direct and indirect evidence suggests that inshore reefs from the Great Barrier Reef (GBR) are showing signs of regional decline following European settlement in the mid 18th century, it has proven difficult to ascertain the link between anthropogenic disturbance and coral degradation on a regional scale.

The aims of this work (MTSRF Project 1.1.3b) were to identify the role of light and water temperature as drivers of change in seagrass meadows of the northern Great Barrier Reef. Experimental approaches as well as field investigations were undertaken.

The purpose of this study is to quantify spatial and temporal changes in the density of crown-of-thorns starfish and benthic cover in the Great Barrier Reef. Broad-scale manta tow surveys have been conducted by the Long-Term Monitoring Program (LTMP) of the Australian Institiute of Marine Science since 1986, counting crown-of-thorns-starfish (COTS, Acanthaster planci).
This dataset consists of 31 monitoring sites in the Tully-Ingham area. Sites have various levels of rainforest invasion. Each site has a vegetation strata species list and counts of each species in each strata. Trees with stems > 10cm Diameter Breast Height (DBH) are identified and their DBH and height are measured. Date of survey May-July 2014.
This dataset shows the concentrations of multiple herbicides remaining over time in a simulation flask persistence experiment conducted in 2013.
The aim of this study was to quantify the persistence multiple herbicides in a standard flask experiment. Time it takes for degradation of half of this herbicide is termed the "half-life". The half-life can be used to help develop environmental risk assessments.
Methods:
This dataset shows the geology of the Torres Strait region. The polygons in this dataset are a digital representation of the distribution or extent of geological units within the area. Polygons have a range of attributes including unit name, age, lithological description and an abbreviated symbol for use in labelling the polygons. These have been extracted from the Rock Units Table held in the Department of Natural Resources, Mines and Energy Merlin Database.

This dataset shows the broad geology of the Wet Tropics of Queensland and surrounding areas from Ayr up to north of Cooktown. It is a combination of the "Geology of the Wet Tropics Bioregion (WTMA)" dataset (WtmaGeology) from the Vegetation mapping of the Wet Tropics and the state wide Regional Ecosystem mapping by the Queensland Government.
Benthic organisms were surveyed annually on fixed sites in one habitat on each of 47 selected core survey reefs from 1993 to 2005 in 6 regions throughout the Great Barrier Reef (GBR). Surveys were undertaken at 3 sites per reef, with 5x50m transects surveyed per site.In 2004 a new zoning plan was implemented in the Great Barrier reef Marine Park and in 2006 the pattern of surveys was changed. The original set of reefs (47) are surveyed in odd years (e.g. 2007) and a different set (56 reefs) are surveyed in even years.



